Bring the potential of ROZLYTREK® to life
ROZLYTREK delivers clinically meaningful responses in NTRK fusion+ solid tumours, irrespective of baseline CNS metastases1,2
ROZLYTREK delivers clinically meaningful responses in NTRK fusion+ solid tumours, irrespective of baseline CNS metastases1,2
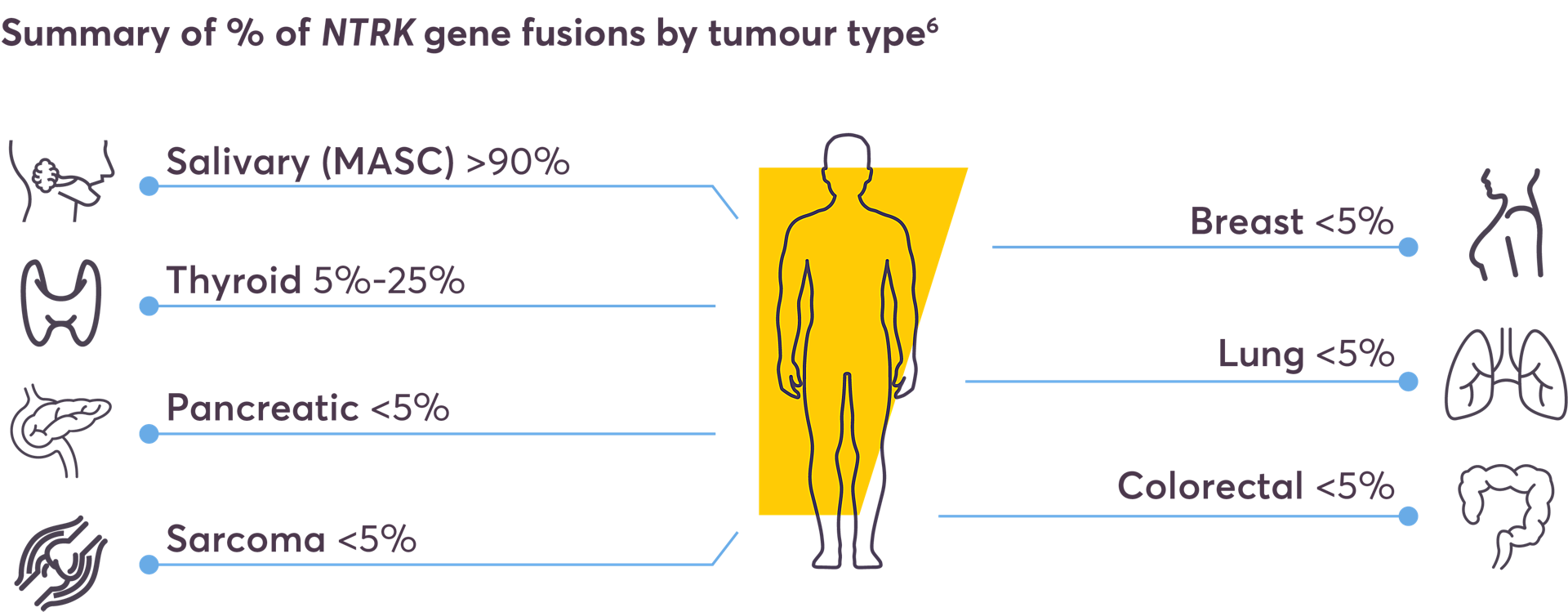
NTRK fusions have emerged as actionable biomarkers in at least 25 types of tumours3–5
The efficacy of ROZLYTREK for patients with NTRK fusion+ solid tumours was evaluated in three Phase I and II trials1,7
Study design
Efficacy was evaluated in 74 adult patients with PI3K NTRK fusion+ solid tumours1,7

* As evaluated by Blinded Independent Control Review.
† Three patients were enrolled into dose-escalation studies.
‡ With ≥6 months of follow up from date of first dose.
Safety was evaluated in 504 adult and paediatric patients across multiple biomarkers and tumour types as an integrated analysis of 4 clinical trials: ALKA-372-001, STARTRK-1, STARTRK-2 and STARTRK-NG1
ROZLYTREK was studied across a range of tumour types1

Patient characteristics
ROZLYTREK was studied in a tumour-agnostic cohort of 74 adult patients with NTRK fusion+ solid tumours1
Efficacy
ROZLYTREK delivered clinically meaningful responses in NTRK fusion+ solid tumours, irrespective of baseline CNS metastases1,2
CNS efficacy
ROZLYTREK crosses the blood–brain barrier and results in a clinically meaningful response in NTRK fusion+ patients with CNS metastasis1,7,8
ROZLYTREK is a weak substrate of P-glycoprotein and therefore is able to achieve clinically meaningful concentrations in the CNS1,9
ROZLYTREK offers high progression-free rates in the CNS8
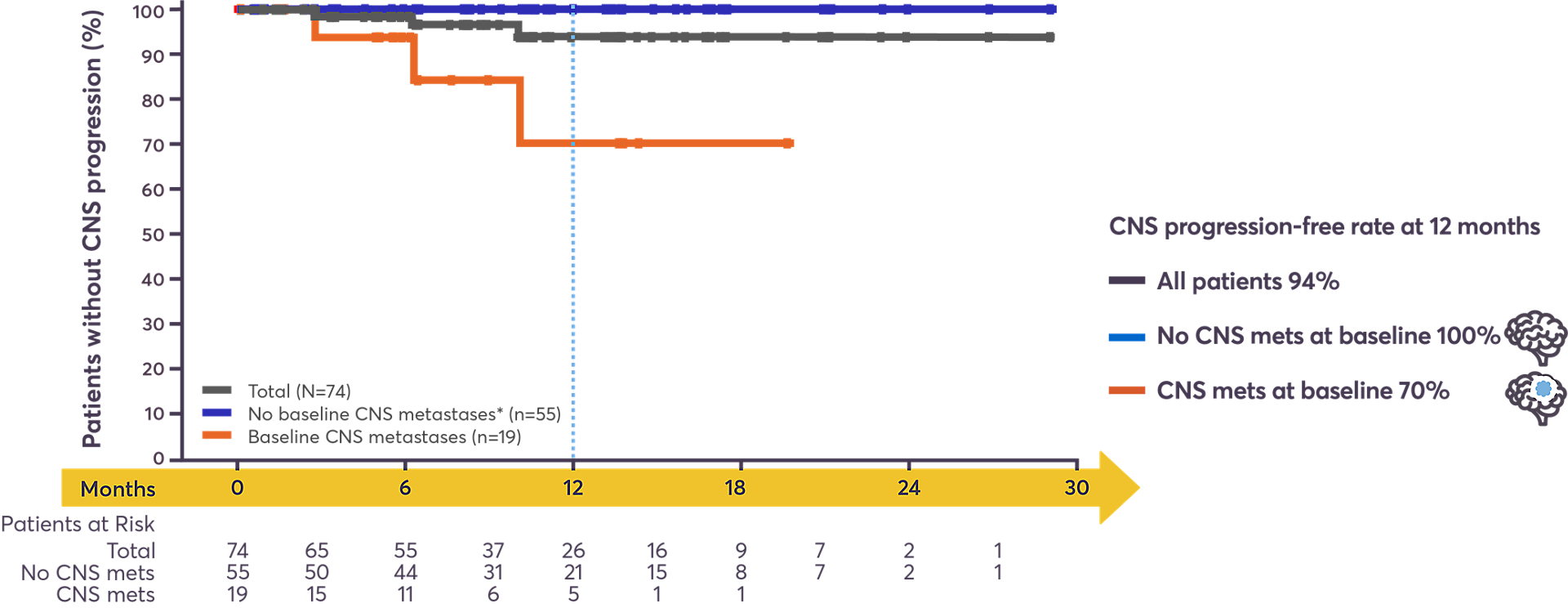
Baseline CNS metastases assessed by investigator. Time to CNS progression: only confirmed CNS progression counted as an event (death censored).
*As regular CNS scans were not mandated by the protocol, CNS follow-up of patients without baseline metastases was not comprehensive but based on symptomatic progression or routine CNS scans where customary.
The only TRK inhibitor designed to remain and deliver benefit to the CNS1,2,8
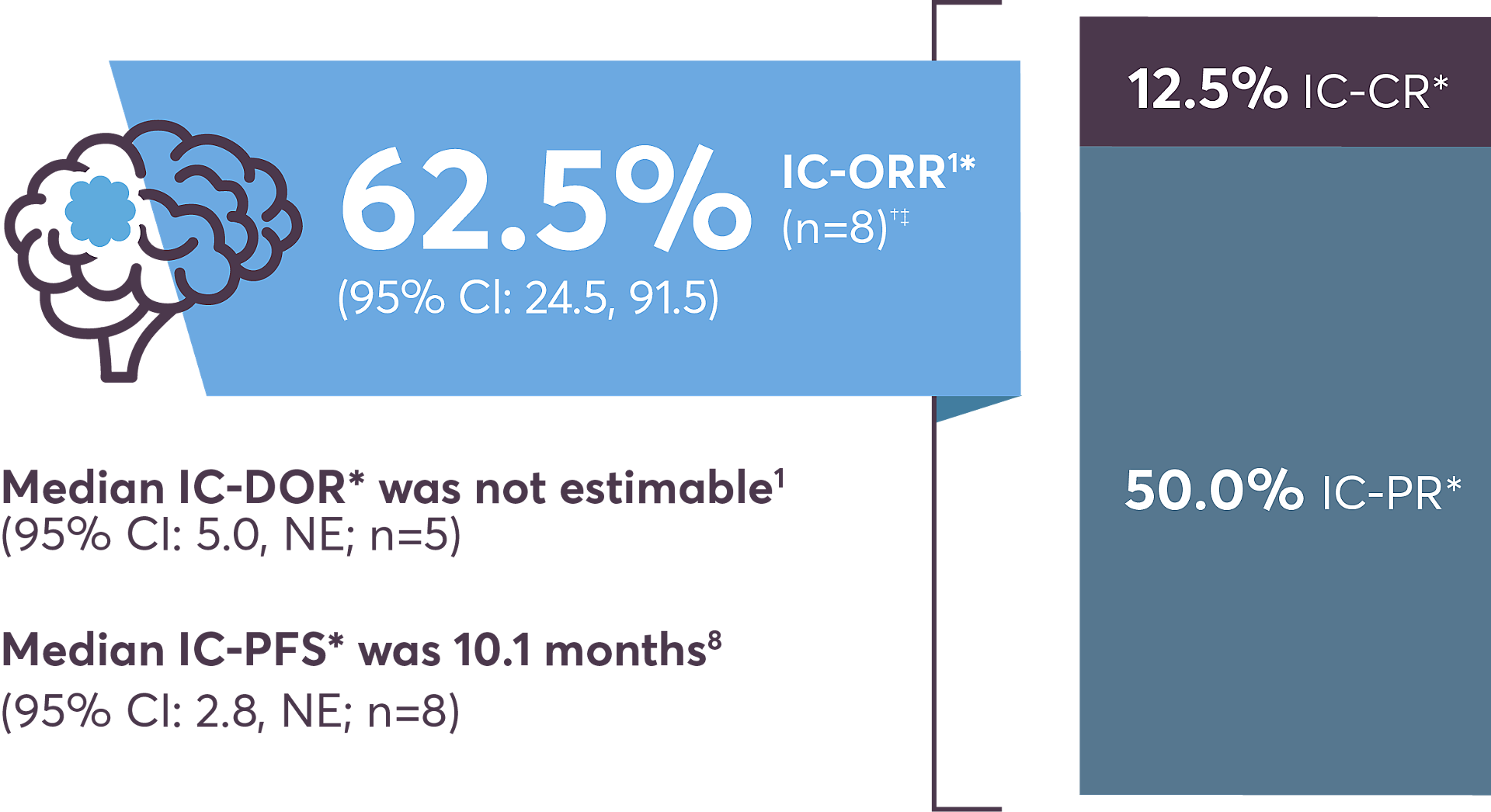
* As evaluated by Blinded Independent Central Review.
† Patients with measurable baseline CNS metastases
‡ Four of eight patients had received intracranial radiotherapy to the brain within 2 months of their first dose of ROZLYTREK
IC-ORR shows efficacy in the brain10

ROZLYTREK delivers clinically meaningful responses in NTRK fusion+ solid tumours, irrespective of baseline CNS metastases:1,2
This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions. See section 4.8 of the SmPC for details on how to report adverse reactions.
Footnotes
BICR, Blinded Independent Control Review; CI, confidence interval; CNS, central nervous system; CR, complete response; DOR, duration of response; ECOG, The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; ESMO, European Society for Medical Oncology; HR, hazard ratio; IC-CR, intracranial complete response; IC-DOR, intracranial duration of response; IC-ORR, intracranial objective response rate; IC-PR, intracranial partial response; ITT, intent-to-treat; MASC, mammary analogue secretory carcinoma; Miss, missing; MRP, multidrug resistance protein; NA, not applicable due to small number or lack of response; NE, not estimable; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; NTRK, neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase; ORR, objective response rate; OS, overall survival; PD, progressive disease; PFS, progression-free survival; P-gp, permeability-glycoprotein; PR, partial response; QD, once-daily; ROS1, c-ros oncogene 1; TRK, tropomyosin receptor kinase; TTD, time to treatment discontinuation; TTNT, time to next treatment.
References
- ROZLYTREK Summary of Product Characteristics, 2020.
- Rolfo C, et al. Efficacy and safety of entrectinib in patients with NTRK fusion-positive (NTRK-fp) solid tumours: an updated integrated analysis. Presented at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting, 29 May – 4 June 2020.
- Amatu A, et al. ESMO Open 2016;1:e000023.
- Lange AM, et al. Cancers (Basel) 2018;10.
- Vaishnavi A, et al. Cancer Discov 2015;5:25-34.
- Cocco E, et al. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2018;15:731–747.
- Doebele RC, et al. Lancet Oncol 2020;21:271–282.
- John T, et al. Intracranial efficacy of entrectinib in patients with NTRK fusion-positive solid tumours and baseline CNS metastases. Presented at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020, 19–21 September 2020.
- Fischer H, et al. Neuro Oncol 2020;22:819–829.
- Data on file. Genentech, Inc.










